2025-26 New Edition Family Medicine Sample Question
FM Prep exam success just got better! With updated questions, clear and concise explanations, and hundreds of visuals designed to support your exam excellence, TrueLearn’s FM Prep SmartBank is the top choice for your ABFM In-Training & Certification examinations.
Here’s what you get with the FM Prep SmartBank 2025-26 New Edition:
- 1,400+ ABFM-style practice questions
- Over 700 new questions added for the 2025-2026 FM Prep Exam
- 170+ high-yield illustrations, visuals and tables
- FM Prep Predictive Assessment Add-On
- 150 all-new questions not included in the SmartBank
- Optional 200-question AOBFP add-on for Osteopathic Residents
Try This FM Prep Sample Question from the 2025-26 New Edition
A 43-year-old woman is brought in to the emergency room by paramedics for evaluation after being found wandering in the snow late at night. She appears disheveled and is dressed in a jacket, pants, and flip-flops. The paramedics have not been able to obtain any history from her but note that she has been talking to herself and to unseen persons throughout her transport to the emergency department. On evaluation, she is found to be hypothermic with a rectal temperature of 90°F. Her feet are cold and pale on the initial exam with cyanosis of the distal aspects of her toes noted. Active rewarming efforts are initiated and she is admitted for further treatment. On the second day of admission, exam findings of her feet appear to have worsened (see picture below).
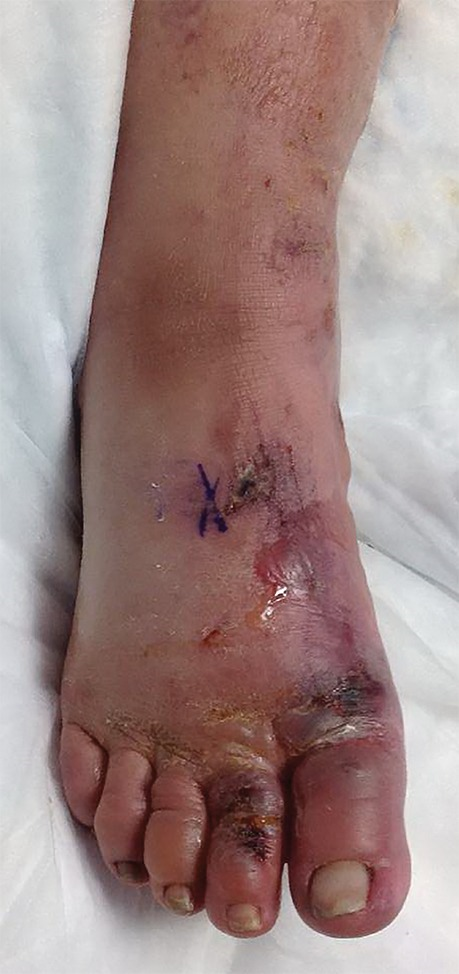
What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Chilblains
- Second-degree frostbite
- Third-degree frostbite
- Fourth-degree frostbite
- Trench foot
Show The Answer Key
Did you get it right? The correct answer is C.
Answer Explanation
The patient in this question had a significant cold exposure without sufficient protection against the elements (wearing flip-flops). She was noted to have cold pale feet on arrival with cyanosis of the toes. Exam findings of her feet from the following day, show hemorrhagic blister formation along with edema and erythema. These exam findings are consistent with third-degree frostbite.
Frostbite is a thermal tissue injury caused by prolonged exposure to temperatures below 32°F. It typically affects the hands or feet, though it may also be seen on the face, perineum, buttocks, or male genitalia. Risk factors for developing frostbite include alcohol use, homelessness, psychiatric illness (such as is likely in this patient), diabetes mellitus, smoking, immobilizing traumatic injury, and illicit drug use. Signs and symptoms of frostbite include initial pallor or discoloration of the skin with paresthesia to complete anesthesia of the affected area. Upon rewarming, severe pain may occur and further changes to the tissue may be noted as microscopic cellular injuries become visible, with edema and erythema developing. Depending on the degree and extent of damage, blister formation (ranging from clear in 2nd degree to hemorrhagic in 3rd degree), worsening edema, and signs of tissue necrosis may develop. These signs may develop over a period of hours and the full extent of the injury may not be apparent until after 24-48 hours.
Frostbite can be classified into 4 different degrees.
| 1st degree | Superficial damage with edema and erythema without blistering |
| 2nd degree | Worsening superficial damage with edema, erythema, clear to milky blister formation. There is no tissue loss |
| 3rd degree | Deeper tissue damage with more significant edema, erythema, hemorrhagic blister formation, and cyanotic skin discoloration |
| 4th degree | Profound tissue damage that may have a deep red mottled appearance to gangrenous necrotic appearance. because of the extent of damage to the dermis and epidermis, there is no blistering and there is no edema |
 .
.
Incorrect Answer Explanations
Answer A: Chilblains, also known as pernio, is a thermal injury that occurs in some individuals after exposure to cold and damp environments. It manifests as localized macules, patches, papules, and nodules that are erythematous, edematous, and painful. While typically present only on fingers and toes, lesions may also occur anywhere else on the lower extremities as well as on the face. Its pathogenesis is not completely understood, but it will typically manifest within 12-24 hours after cold exposure and resolve within a few weeks. Young and middle-aged women are the most commonly affected. Exam findings do not support the diagnosis of Chilblains.
Answer B: Second-degree frostbite is characterized by more significant superficial tissue damage compared with first-degree frostbite. There will be edema, erythema, and clear to milky blister formation. This patient’s exam findings are more consistent with third-degree frostbite.
Answer D: Fourth-degree frostbite describes a deep tissue damage. Exam findings will show a deep red mottled to frankly gangrenous necrotic appearance after re-warming. With the extent of damage to the dermis and epidermis, no blistering, and minimal if any edema occurs. The patient does not have these findings on exam.
Answer E: Trench foot is a non-freezing cold injury that is caused by prolonged exposure to cold, wet conditions. As in frostbite, the injured tissue may initially appear pale and will be numb, but later will become erythematous, edematous, and quite painful. This injury can be differentiated from frostbite by the temperatures to which the tissue was exposed. While in frostbite the tissue is exposed to freezing temperatures < 32°F, non-freezing cold injuries such as trench foot occur at temperatures typically between 32-59°F. The patient in this question had an exposure to freezing temperatures, thus frostbite would be the more accurate diagnosis.
Bottom Line
Frostbite is a thermal cold injury from exposure to freezing temperatures with different degrees of damage depending on duration and extent of exposure. Early on, the different degrees of injury may appear similar and may only be differentiated well after rewarming has taken place.