Free Anesthesiology Assistant Sample Questions
See why TrueLearn is a trusted resource for the NCCAA Anesthesia exam. We understand that it’s all about the content. That’s why we have high-yield anesthesiology assistant practice questions written and screened by high-performing authors that are updated on a regular basis to ensure our SmartBanks stay up-to-date with NCCAA exam blueprint changes.
First Free Anesthesiology Assistant Question (From the 2025-26 SmartBank)
Which of the following describes the volume of gas remaining in the lungs at passive end expiration?
A. Closing capacity
B. Expiratory reserve volume
C. Functional residual capacity
D. Residual volume
E. Vital capacity
Answer and Explanations
Did you get it right? The correct answer is C.
The amount of gas remaining in the lungs at the end of a normal, tidal volume exhalation is the functional residual capacity (FRC). The FRC is comprised of the expiratory reserve volume (ERV) and the residual volume (RV).
Functional residual capacity is the primary determinant of oxygen reserve in humans when apnea occurs. As humans age, the lung parenchyma loses its elasticity and becomes more compliant, resulting in an age-related increase in FRC. Factors that decrease FRC include obesity, pregnancy, pulmonary edema, pulmonary fibrosis, pleural effusions, and kyphoscoliosis.

Individual lung volumes are noted in blue and lung capacities (the sum of 2 or more individual lung volumes) are noted in red. Expiratory reserve volume* (ERV*) indicates the volume that is forcefully exhaled from the lungs when pulmonary conditions promote early airway closure and atelectasis. (Volumes: RV = residual volume, ERV = expiratory reserve volume, TV = tidal volume, IRV = inspiratory reserve volume, ERV* = expiratory reserve volume with atelectasis, CV = closing volume; Capacities: VC = vital capacity, IC = inspiratory capacity, TLC = total lung capacity, FRC = functional residual capacity, CC = closing capacity).
Incorrect Answer Explanations
Answer A: Closing capacity is the volume at which the airways begin to close. Closing capacity increases with age and typically exceeds FRC in the mid 60’s. Closing capacity will eventually exceed tidal volume in elderly patients. This is functionally similar to the lung mechanics of neonates and infants.
Answers B: The ERV is the largest volume of gas that can be forcibly exhaled after the end of a normal tidal exhalation. It is measured by subtracting the RV from the FRC.
Answer D: Residual volume is the gas remaining in the lungs after maximal exhalation.
Answer E: The vital capacity is comprised of the tidal volume, inspiratory reserve volume, and the expiratory reserve volume. In other words, it is the volume of air that can be maximally exhaled after a maximum inhalation. Vital capacity is typically 60 ml/kg.
Bottom Line
Functional residual capacity is the volume of gas remaining in the lungs at passive end expiration. Furthermore, FRC is the primary determinant of oxygen reserve in humans when apnea occurs.
For more information:
- American Board of Anesthesiology Keyword. “FRC: definition”
- Barash, Clinical Anesthesia, 6th edition, pp. 247-248, 883, 1232.
Second Free Anesthesiology Assistant Question
Which of the following is NOT a common complication of an axillary block?
A. Hematoma
B. Intravascular injection
C. Pneumothorax
D. Postoperative neuropathy
E. Systemic toxicity
Answer and Explanations
Pneumothorax is NOT a common complication of an axillary brachial plexus block. This is a known complication of a supraclavicular block (SCB) where it occurs up to 6% of the time.
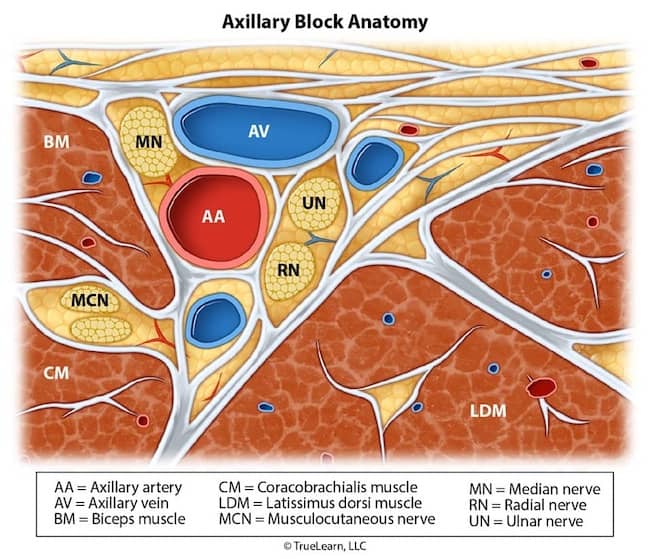
Cross-sectional anatomy of the right axillary nerve block. The median, ulnar, and radial nerves are bundled with the axillary artery within the axillary sheath. Puncture of the axillary artery or vein may cause hematoma formation. Simultaneous nerve injury from needle trauma may also occur owing to the close proximity of the proximity of structures within axillary neurovascular bundle. Mc = Musculocutaneous nerve, Me = Median nerve, U = Ulnar nerve, R = Radial nerve, A = Axillary artery, V = Axillary vein, B = Biceps brachii muscle, T = Triceps brachii muscle, C = Coracobrachialis, D = Deltoid muscle, H = Humerus, Dotted line = outline of Axillary sheath
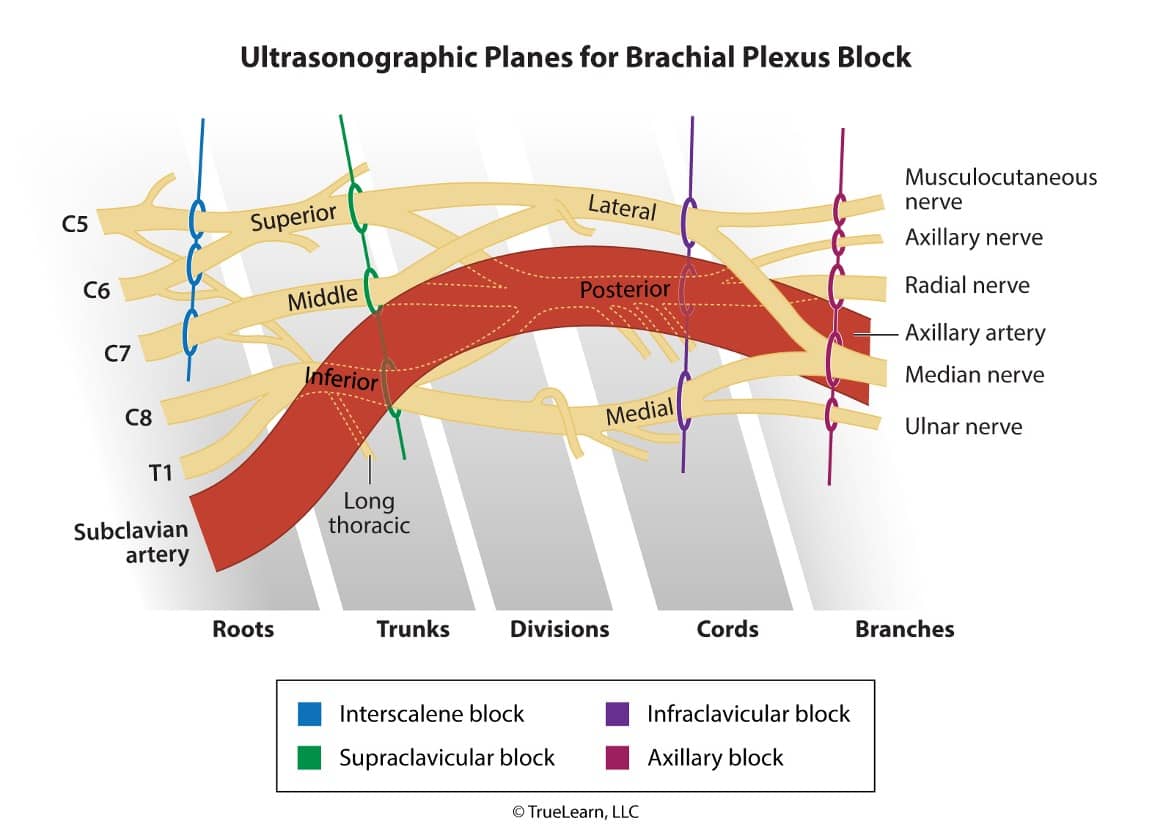
The axillary block is highlighted in RED in this illustration depicting the sections of the brachial plexus and associated structures typically encountered during ultrasound guidance (dotted lines). The terminal nerve branches visualized with ultrasound are encircled. The axillary artery is also seen within this plane. Note the proximity of the median, radial, and ulnar nerves to the axillary artery. The axillary sheath (not pictured) encases these structures. The musculocutaneous nerve is not contained within the sheath and must be anesthetized separately. (UT = upper trunk, MT = middle trunk, IT = inferior trunk, ScA = Subclavian artery, AxA = Axillary artery, Mc = Musculocutaneous nerve, Me = Median nerve, R = Radial nerve, U = Ulnar nerve).
Did you get it right? The correct answer is C.
Incorrect Answer Explanations
Answer A: Hematoma may form secondary to puncture of the axillary artery.
Answers B & E: Systemic local anesthetic toxicity may occur as a result of intravascular injection.
Answer D: Postoperative neuropathy can result from nerve injury due to needle trauma or intraneural injection.
Bottom Line
Known complications of an axillary block include systemic local anesthetic toxicity, hematoma, and postoperative neuropathy. Pneumothorax is a known complication of a SCB, not an axillary block.
For more information:
- Brown, Atlas of Regional Anesthesia, 3rd edition, pp. 63-70.
- Stoelting, Basics of Anesthesia, 5th edition, pp. 278-279.
- Atchabahian A. Ultrasound-Guided Supraclavicular block. Journal of the New York School of Regional Anesthesia (NYSORA), 13: 20-26 (2009).
- American Board of Anesthesiology Keyword. “Axillary Block: Complications”
Get More Free NCCAA Practice Questions
Ready for more free anesthesiology assistant sample questions? Sign up for a free trial of our SmartBank.