Free Sample COMAT Practice Questions
We understand that it’s all about the content. That’s why we have high-yield practice COMAT practice questions written and screened by physician authors that are updated on a regular basis to ensure our SmartBanks stay up-to-date with exam blueprint changes.
Below is a free practice question for general surgery, however our COMAT qbank contains questions for all 8 subjects.
Your First Free COMAT Practice Question
A 37-year-old gravida 2 para 1 woman at 20 weeks’ gestation presents to the office for a routine prenatal visit. She reports no vaginal bleeding or leakage of fluid. Her previous pregnancy resulted in a spontaneous vaginal delivery at term. Vital signs are within normal limits. Ultrasonography reveals that the placenta is covering the internal cervical os and her cervical length is measured at 4.0 cm. The most appropriate next step in management is to
- A. admit the patient to the hospital for additional evaluation and monitoring
- B. continue routine obstetric care
- C. perform a cervical cerclage
- D. recommend complete bed rest for the remainder of the pregnancy
- E. schedule the patient for weekly ultrasound evaluation
The Correct Answer and Explanation
The correct answer is: B
The only abnormality seen on this patient’s examination is the presence of a placenta previa on ultrasound. Given that most cases of placenta previa will resolve spontaneously, the patient should continue routine obstetric care and undergo repeat ultrasound imaging in the third trimester.
Placenta previa occurs when placental tissue covers a portion or all of the cervix and is typically diagnosed on routine prenatal ultrasound around 18-20 weeks’ gestation. While most cases will occur in the absence of any risk factors, the development of a placenta previa is more likely in the setting of multiple gestations and/or a prior cesarean delivery. At baseline, most patients are asymptomatic; however, partial placental detachment can lead to severe painless vaginal bleeding > 20 weeks’ gestation.
Following additional diagnosis, initial management involves routine obstetric care with repeat ultrasound imaging performed at ≥ 28 weeks’ gestation. Given that there is a significant risk of causing placental detachment with cervical manipulation, pelvic rest is recommended and patients should be advised to abstain from sexual intercourse. Additionally, a digital cervical examination should not be performed in the setting of a known or suspected placenta previa. Lastly, patients should be advised to immediately present to the hospital for any vaginal bleeding.
Approximately 90% of cases will resolve spontaneously as the lower uterine segment lengthens and/or the placenta grows towards the fundus as pregnancy progresses. As such, most patients with a placenta previa diagnosed early in pregnancy will still be able to undergo vaginal delivery. However, vaginal delivery should not be attempted in the setting of a persistent placenta previa and patients should instead be scheduled for a cesarean delivery at 36-37 weeks’ gestation.
Placenta Previa
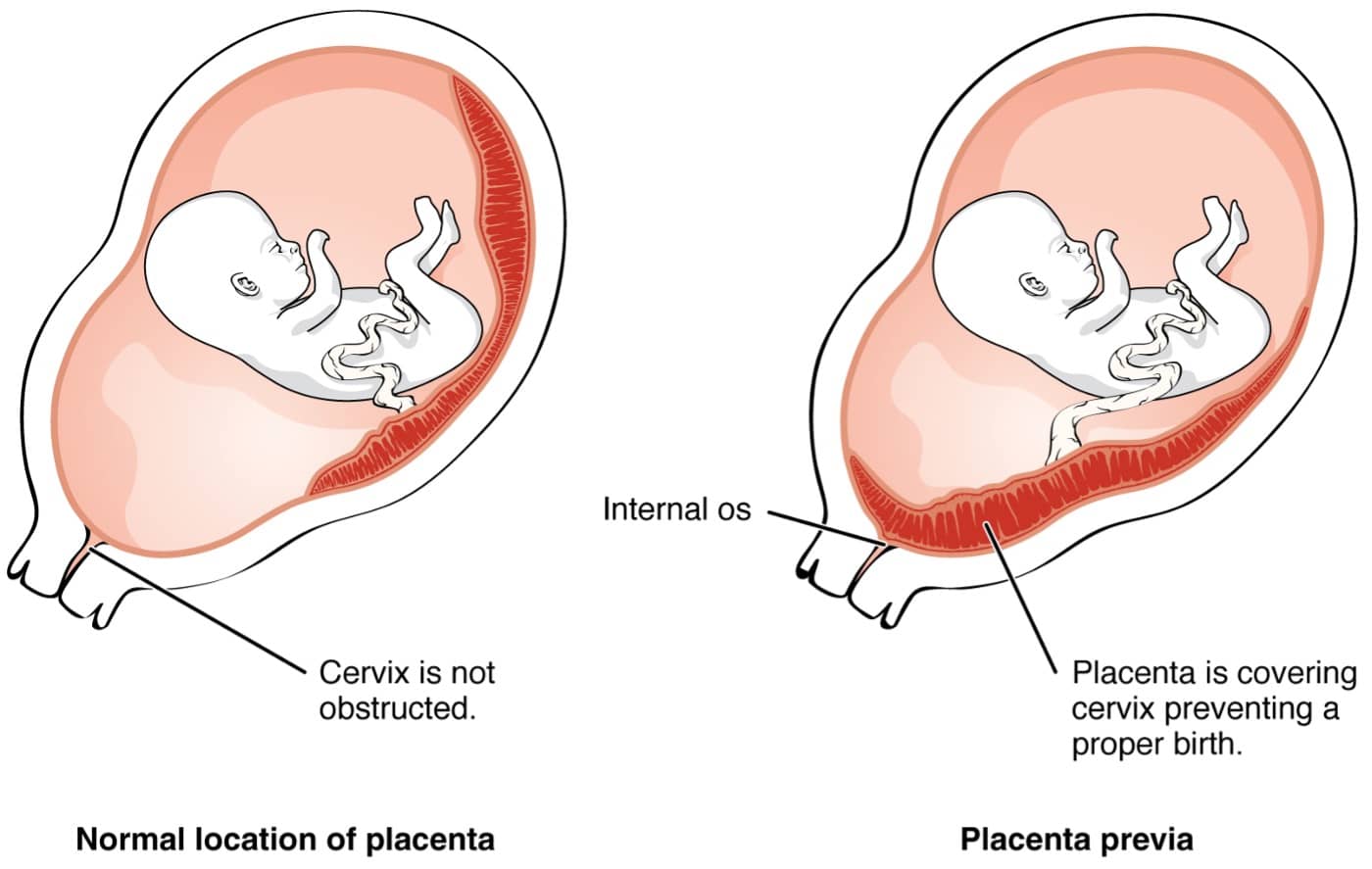
| Risk factors | In vitro fertilization Multiple gestations Prior cesarean delivery or placenta previa |
| Clinical manifestations | Painless vaginal bleeding > 20 weeks’ gestation |
| Diagnosis | Transabdominal ultrasound followed by transvaginal ultrasound |
| Initial management | ~ 90% will resolve spontaneously Continue routine obstetric care No intercourse or digital cervical examination |
| Delivery | If persistent, schedule Cesarean delivery at 36-37 weeks gestation |
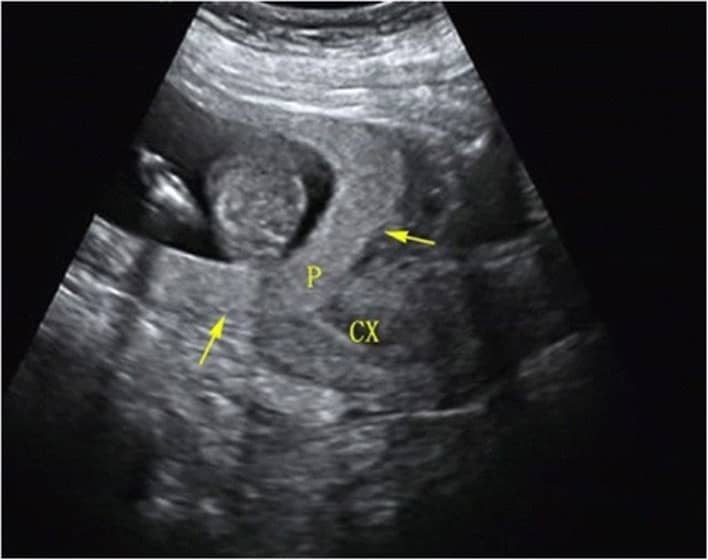
Below is a sonographic image of a complete placenta previa, marked by (P), covering the cervix (CX).
Wrong Answer Explanations
Answer A: Patients with a known (or suspected) placenta previa should be admitted to the hospital for any bleeding episode. However, as this patient is not bleeding, there would be no reason to admit her to the hospital at this time.
Answer C: A cerclage is used to manage cervical insufficiency and is typically indicated for patients with a history of second-trimester deliveries or a short cervix. A shortened cervix is defined as a cervical length of ≤ 2.5 cm and as such, this patient’s cervical length of 4 cm would not warrant cerclage placement.
Answer D: Complete bed rest is not appropriate management of a placenta previa and would increase the risk of venous thromboembolism due to venous stasis. However, it is recommended that patients be advised to abstain from sexual intercourse. Additionally, a digital cervical examination should not be performed as cervical manipulation may result in placental detachment.
Answer E: Weekly ultrasound evaluation is not necessary for a placenta previa given that there is unlikely to be any significant change week to week. Instead, the patient can undergo repeat ultrasound evaluation typically around (or shortly after) 28 weeks gestation. If the placenta previa is persistent at this time, scheduled Cesarean delivery should be discussed.
Bottom Line
Placenta previa is typically diagnosed with routine prenatal ultrasound around 18-20 weeks gestation. Initial management involves routine obstetric care with avoidance of both sexual intercourse and digital cervical examinations. Most cases will resolve spontaneously; however, patients with a persistent placenta previa should undergo scheduled cesarean delivery at 36-37 weeks gestation in order to decrease the risk of antepartum hemorrhage.
COMBANK Insight
Both placenta previa and vasa previa (a condition where fetal vessels overlie the cervix) are typically diagnosed around 18-20 weeks gestation during routine fetal anatomy ultrasound. When persistent, both of these conditions will require scheduled cesarean delivery given the high risk of antepartum hemorrhage. However, most placenta previas resolve spontaneously, and if resolution occurs, the patient may undergo a vaginal delivery.
For more information, see:
- Management of placenta previa: UpToDate
- Placenta previa: epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, morbidity and mortality: UpToDate
- Placenta Previa: StatPearls
Image sources:
Download More Free COMAT Practice Questions
Fill out this form to get more free sample questions for your COMAT exam prep. And whenever you’re ready, come back for a COMAT SmartBank subscription.
![[On-Demand Webinar] COMLEX Level 2 PE Overview](https://truelearn.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/Featured-Image_Webinar.png)
