Free Sample Emergency Medicine Questions, with Answers
See why TrueLearn is a trusted resource for thousands of medical students and residents. At TrueLearn, we understand that it’s all about the content. That’s why we have high-yield emergency medicine practice questions written and screened by high-performing physician authors that are updated on a regular basis to ensure our SmartBanks stay up-to-date with exam blueprint changes. Below are two free emergency medicine sample questions, with complete answers. One is from our ABEM ITE question bank and the second is from our ABEM Qualifying q-bank.
Free ABEM ITE Sample Question
A 32-year-old male presents to the emergency department with complaints of hallucinations, abnormal thoughts, disorganized behavior and emotional withdrawal that has been worsening over the past 12 months. The patient has a history of schizophrenia. Vital signs are stable and on history and physical examination the patient is poorly attentive with a flat affect. Labwork, imaging and diagnostics are unremarkable. Which of the following is true regarding schizophrenia?
- A. Poor parenting may lead individuals to develop this condition
- B. Schizophrenic individuals tend to seek medical attention themselves after hallucinations develop
- C. Symptoms tend to begin to manifest by late adolescence
- D. The cause of this illness likely has to do with psychological stressors
Answer and Explanations
Did you get it right? The correct answer is C.
Schizophrenia is one of the most prevalent psychoses presenting to the emergency department.
Commonly, these patients feature a deterioration in functioning, positive symptoms including hallucinations, delusions, disorganized speech, disorganized behavior, and paranoia. It is important to remember that negative symptoms may also present which include a blunted affect, emotional withdrawal, a lack of spontaneity, and attentional impairment.

Diagnostic criteria in DSM V for schizophrenia. It should be noted that the subtypes of schizophrenia were removed (paranoid, simple, catatonic, disorganized) in the transition from DSM IV to V. This makes the diagnosis of schizophrenia a very broad and hard to understand illness for both patients and practitioners.
These patients usually have a relative absence of a mood disorder. It is thought that schizophrenia is likely a collection of psychological disorders that share a common final pathway.
There is no evidence that psychological stress or poor parenting is responsible for causing this illness. Symptoms usually begin in late adolescence but onset can theoretically occur at any age. A prodromal phase is usually noted which includes a gradual deterioration in function as well as the development of active delusions or hallucinations. This compounds the patient’s issues with social involvement leading to social withdrawal, odd behavior or speech, and difficulty in functioning at school or work.
Families caring for a patient with schizophrenia rarely seek medical attention until they are actively experiencing psychosis. Schizophrenic patients themselves seldom seek care at all because they lack insight and do not realize that their perceptions, thoughts and behaviors are abnormal.
Treatment includes both medical therapy as well as counseling as tolerated. These patients should be screened for illicit substances as well as underlying medical conditions which may prevent similarly including delirium caused by infection or other metabolic derangements.
These patients additionally should also be screened for suicidal or homicidal ideation and risk stratified by mental health as needed. Resources should be provided to both the patient and family. Successful treatment of schizophrenia is the establishment of a reliable care network for the patient. Although functioning may decline over time, patients should be encouraged as much as possible to follow-up with outpatient resources to prevent further functional decline.
Incorrect Answer Explanations
Answer A: Although poor parenting may lead to poor coping skills, there has never been a link between parenting and the onset of schizophrenia.
Answer B: Schizophrenic individuals rarely seek medical attention on their own due to a relative lack of insight.
Answer D: Although psychological stressors may contribute to a patient’s ability to handle continued functional status there has never been a link between stress causing the onset of schizophrenia.
Bottom Line
Schizophrenia is a difficult to treat medical condition which must commonly be acutely managed in the emergency department.
For more information, see:
Tintinalli’s Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide, 8e Chapter 286: Mental Health Disorders: ED Evaluation and Disposition
Get More Free ABEM ITE Practice Questions
Free TrialFree ABEM Qualifying Sample Question
A 23-year-old gravida 2, para 1 woman at 10-weeks gestation presents to the emergency department with complaints of sudden onset moderate and intermittent LLQ abdominal pain starting prior to arrival. The patient has no history of pelvic inflammatory disease or ectopic pregnancy. The patient notes no difficulty with eating or drinking and denies any surgical history. Ultrasound reveals normal adnexa and a normal intrauterine gestation. B-hCG testing reveals a quantitative level of 1231 U/mL. The patient appears very uncomfortable on exam and exhibits tenderness with guarding to palpation in the left lower quadrant. Which of the following should be performed next given the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Consult with OB/GYN for possible surgical intervention
- B. Provide analgesia and have the patient follow-up with OB/GYN within the next month
- C. Perform CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis for further evaluation
- D. Perform MRI of the abdomen and pelvis for further evaluation
Answer and Explanations
The correct answer is: A
The correct answer is to Consult with OB/GYN for possible surgical intervention.
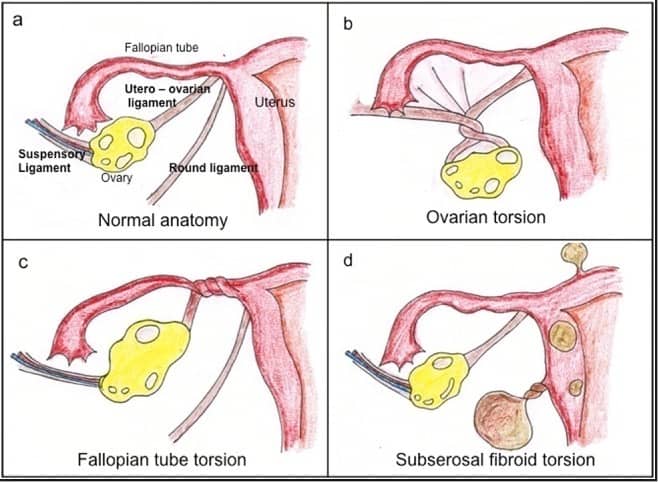
Approximately 1/5 of ovarian torsion cases occur during pregnancy, with the majority being within the first trimester. The increase in the size of the ovaries secondary to increased levels of estrogen is thought to play a role as is increased ligamentous laxity. The diagnosis is a true surgical emergency and is often missed secondary to a vague presentation of moderate, intermittent lower quadrant abdominal pain.
Ultrasound is largely non-specific, and up to 60% of patients with ovarian torsion have a normal ultrasound. Arterial flow is largely normal in these studies likely because arterial insufficiency is a late finding. Some studies have shown increased sensitivity for torsion by assessing venous flow, however despite advances in ultrasound technology most of these patients have normal ultrasound findings.
If clinically concerned, consultation with OB/GYN for possible surgical management is reasonable given the severity of this diagnosis. If the ovary becomes persistently torsed, rapid ischemia and ovary death can ensue. Therefore, these patients should ideally be evaluated by specialty care before discharge if available.
Incorrect Answer Explanations
Answer B: Although discharge is not completely out of the question, this would not be the best answer. Consultation while in the emergency department with OB/GYN would be the best next step followed by short-term follow-up with OB/GYN, ideally with an appointment made from the emergency department within the next 1-2 days. A month follow-up may be too long.
Answer C: CT scan should obviously be avoided in pregnancy, however if OB wishes to have this study performed the risks and benefits should be explained to the patient before a decision is made. This is not the best next step as the question asks.
Answer D: MRI is a possible imaging modality, however consultation with OB/GYN should be performed first.
Bottom Line
Patients suspicious for ovarian torsion should be seen by specialty care as soon as possible.
TrueLearn Insight
“Next step” questions are notoriously difficult secondary to the “shotgun” nature of a real emergency department.
For more information, see: Tintinalli 8th edition, Chapter 99 Comorbid Disorders in Pregnancy

