Free NAPLEX Sample Questions
See why TrueLearn is a trusted resource for thousands of pharmacy students. At TrueLearn, we understand that it’s all about the content. That’s why we have high-yield pharmacy practice questions written and screened by high-performing pharmacist authors that are updated on a regular basis to ensure our SmartBanks stay up-to-date with exam blueprint changes. Below are a couple free NAPLEX sample questions so you can see what we mean.
Your First Free NAPLEX Sample Question
Which medication has a US Boxed Warning for the potential to cause an increased risk of serious adverse cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction and stroke?
- A. Celebrex
- B. Empagliflozin
- C. Colchicine
- D. Wellbutrin
- E. Duloxetine
Answer and Explanation
The correct answer is: A
All nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), including celecoxib (Celebrex) have US Boxed Warnings for an increased risk of serious adverse cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction (MI) and stroke. This risk may occur early during treatment, but increases with duration of use.
The relative risk of cardiovascular thrombotic events appears to be similar in those with and without known cardiovascular disease or risk factors for cardiovascular disease. However, the absolute incidence of cardiovascular events has been shown to be higher in patients with known disease or risk factors.
New onset hypertension or exacerbation of hypertension may occur with NSAID use. NSAIDs also can cause sodium and fluid retention, so they should be used with caution in patients with edema. In general, they should be avoided in patients with heart failure or recent MI.
Incorrect Answer Explanations
Answer B: Empagliflozin does not have a US Boxed Warning for the potential to cause an increased risk of serious adverse cardiovascular thrombotic events. In fact, post-hoc analysis of the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial suggests use of empagliflozin in diabetic patients with cardiovascular disease and renal impairment may be associated with decreased cardiovascular mortality.
Answer C: Colchicine is an anti-inflammatory often used to treat gout. Colchicine does not have a US Boxed Warning for the potential to cause an increased risk of serious adverse cardiovascular thrombotic events.
Answer D: Wellbutrin is an anti-depressant used to treat major depressive disorder and seasonal affective disorder. Wellbutrin does not have a US Boxed Warning for the potential to cause an increased risk of serious adverse cardiovascular thrombotic events.
Answer E: Duloxetine is a selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor antidepressant (SSNRI) used to treat depression. Duloxetine does not have a US Boxed Warning for the potential to cause an increased risk of serious adverse cardiovascular thrombotic events.
Bottom Line
All nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), including celecoxib (Celebrex) have US Boxed Warnings for an increased risk of serious adverse cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction and stroke.
Picmonic Memory Anchors: NSAIDS
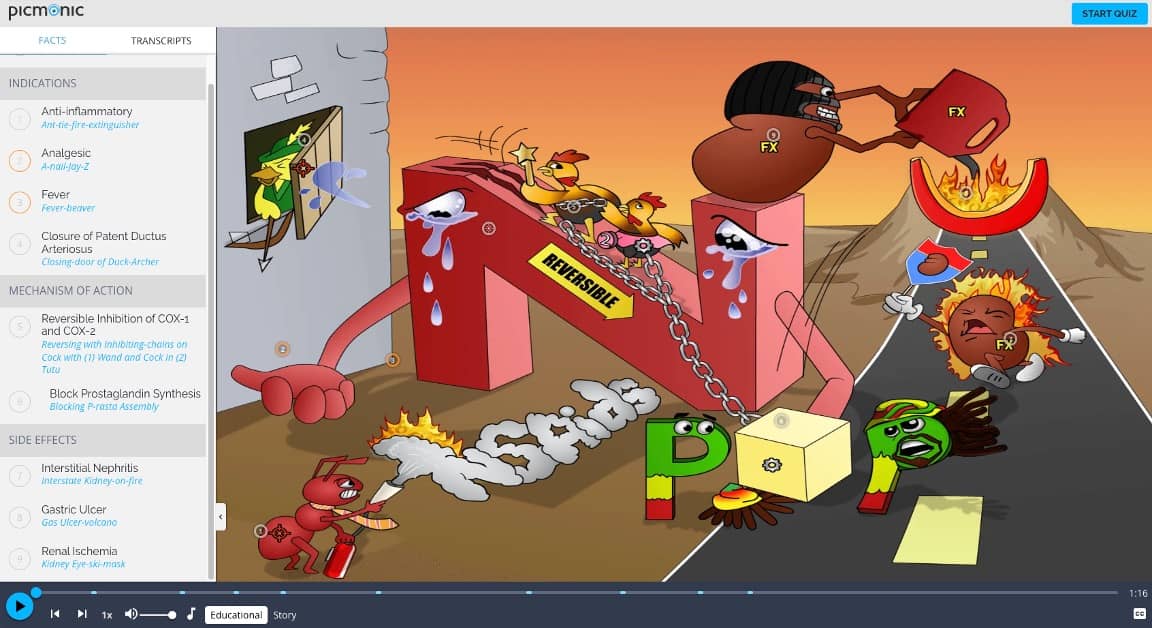
For more information, see:
- Wanner C, Lachin JM, Inzucchi SE, et al; EMPA-REG OUTCOME Investigators. Empagliflozin and clinical outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, established cardiovascular disease, and chronic kidney disease. Circulation. 2018;137(2):119-129.
- Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines. Circulation. 2013;128(16):e240-e327.
- Overview of COX-2 Inhibitors: Celecoxib
- DiPiro. Pharmacotherapy: A Pathophysiologic Approach, 10e. Chapter 60: Pain Management.
Your Second Free NAPLEX Sample Question
A 19-year-old woman presents to her physician for her annual checkup. A full sexually transmitted disease panel was run that resulted in a fourfold increase in nontreponemal test titers. She is otherwise asymptomatic and was unaware she had been exposed to syphilis. The physician is, therefore, suspecting late latent syphilis. What is the first-line recommendation to treat this infection?
A. Azithromycin 1000 mg PO one time
B. Ceftriaxone 250 mg IM one time
C. Doxycycline 100 mg PO BID for 14 days
D. Penicillin G 2.4 million units IM weekly for 3 doses
E. Valacyclovir 1000 mg PO BID for 7-10 days
Answer and Explanation
Latent syphilis is defined as syphilis characterized by seroreactivity without other evidence of primary, secondary, or tertiary disease. Late latent syphilis is latent syphilis where infection occurred more than 12 months ago or an unknown time period.
The recommended treatment is penicillin G 2.4 million units IM weekly for 3 doses. The recommended regimen for primary syphilis is penicillin G 2.4 million units IM in a single dose.
Did you get it right? The correct answer is: D
Incorrect Answer Explanations
Answer A: Azithromycin 1000 mg PO one time is the first-line regimen for chlamydia.
Answer B: Ceftriaxone 250 mg IM one time is the first-line regimen for gonorrhea.
Answer C: Doxycycline 100 mg PO BID for 14 days is an alternative regimen for many infections, but penicillin is the first-line recommendation.
Answer E: Valacyclovir 1000 mg PO BID for 7-10 days is a regimen for genital herpes.
Bottom Line: Asymptomatic with seroreactivity to syphilis is considered latent syphilis. An unknown time period of exposure is late latent syphilis and is treated with 3 doses of penicillin G.
For more information, see:
DiPiro. Pharmacotherapy: A Pathophysiologic Approach, 10e. Chapter 117: Sexually Transmitted Diseases.
![Pharmacist Resume and Cover Letter Mastery [Graduation Success Series]](https://truelearn.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/Featured-Image_Webinar.png)

![How to Increase Your Chances of Getting a Pharmacy Residency [Part II]](https://truelearn.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/Resource-Library-Feature-Images_Blog-1-2.png)