Free NPTE® Sample Practice Questions
We understand that it’s all about the content. That’s why we our have high-yield practice questions written and screened by high-performing physical therapists, and why they are updated on a regular basis to ensure our SmartBanks stay up-to-date with exam blueprint changes.
See what we mean with this free physical therapy board exam sample question.
Your Free NPTE Practice Question
Damage to which peripheral nerve would result in weakness with eversion, and strength within normal limits for all other motions?
- Deep fibular nerve lesion
- Superficial fibular nerve lesion
- Tibial nerve lesion
- Sural nerve lesion
The Answer and Explanation
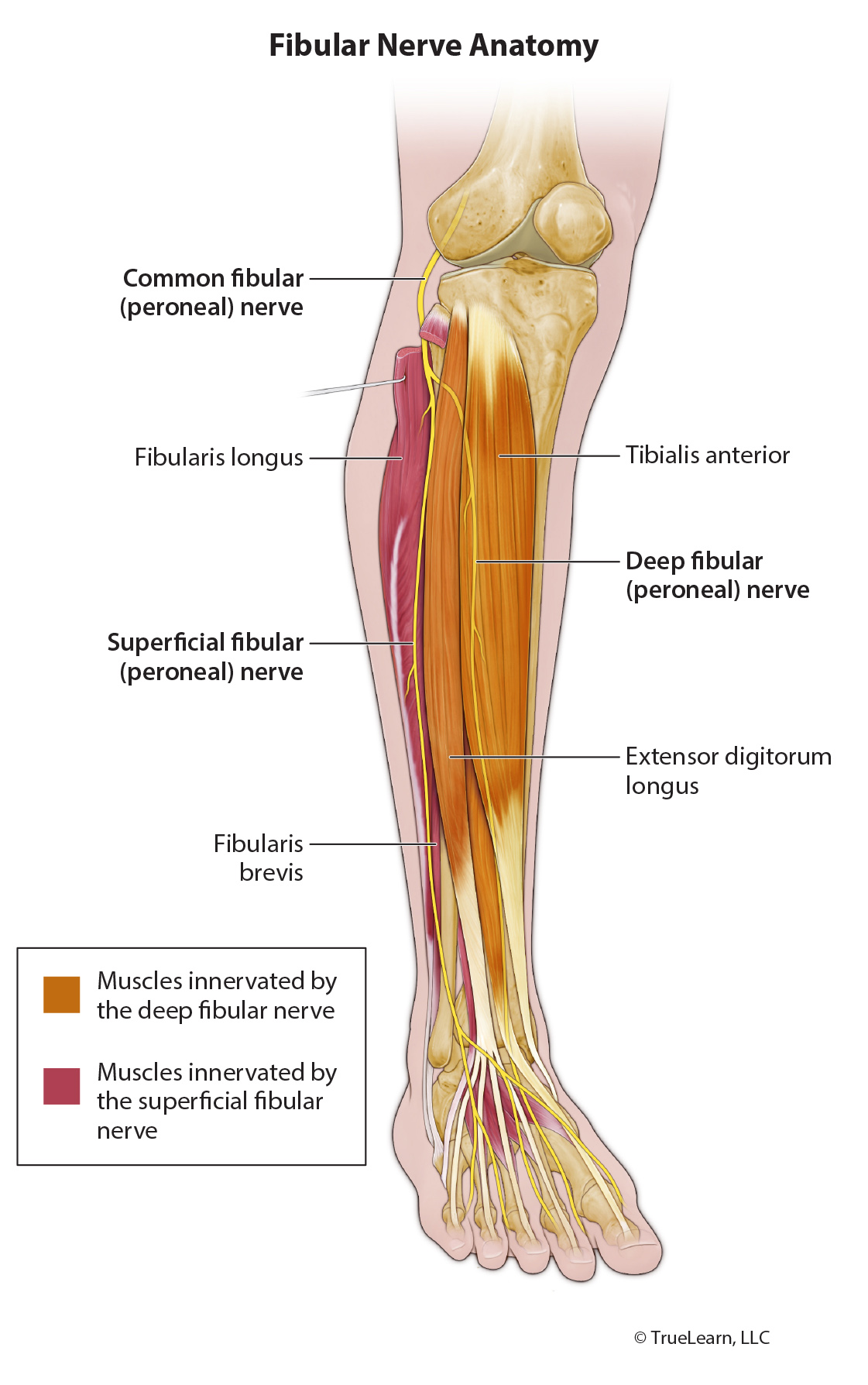
The correct answer is Superficial fibular nerve lesion. The superficial fibular nerve is a branch of the common fibular nerve (L4–S2), which is a branch of the sciatic nerve (L4–S3). It provides motor innervation to the lateral compartment of the lower leg: fibularis longus and fibularis brevis, and sensory innervation to distal anterior leg and dorsum of foot.
Since the fibularis longus and fibularis brevis are the muscles primarily responsible for everting the ankle, a lesion to the nerve supplying them could result in weakness in ankle eversion. They also function to plantarflex the ankle, but there are muscles which are much stronger in plantarflexion that are supplied by the tibial nerve, so this action may not be affected as much by a superficial fibular nerve lesion..
Incorrect Answer Explanations:
Deep fibular nerve lesion
The muscles innervated by the deep fibular nerve do not primarily evert the ankle, so a tibial nerve lesion would not result in ankle eversion weakness. The deep fibular nerve is a branch of the common fibular nerve (L4–S2), which is a branch of the sciatic nerve (L4–S3). It provides motor innervation to the anterior compartment of the lower leg: tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus, extensor digitorum longus, fibularis tertius. It also provides motor innervation to the dorsum of foot: extensor digitorum brevis and extensor hallucis brevis.
Tibial nerve lesion
The tibial nerve (L4–S3) is a major branch of the sciatic nerve (L4–S3). It provides motor innervation to the semimembranosus, semitendinosus, long head of biceps femoris, and part of the adductor magnus. It also provides muscle innervation to the superficial and deep posterior compartments of leg: gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris, tibialis posterior, flexor hallucis longus, and flexor digitorum longus. It also branches into other nerves supplying motor and sensory innervation to the foot.
The muscles innervated by the tibial nerve do not evert the ankle, so a tibial nerve lesion would not result in ankle eversion weakness.
Sural nerve lesion
The sural nerve is a sensory nerve only so it would not affect muscle strength. The sural nerve (L4–S1) is formed by connection of the lateral sural cutaneous communicating branch and the medial sural cutaneous nerve (so it has components of common fibular nerve and tibial nerve), or directly from the lateral sural cutaneous nerve. It provides sensory innervation to the skin of the posterior lower leg and lateral foot.
Bottom Line:
The superficial fibular nerve is a branch of the common fibular nerve (L4–S2), which is a branch of the sciatic nerve (L4–S3). It provides motor innervation to the lateral compartment of the lower leg: fibularis longus and fibularis brevis, and sensory innervation to distal anterior leg and dorsum of foot.


