USMLE Step 2 CK Sample Questions
See why TrueLearn is a trusted resource for thousands of medical students. At TrueLearn, we understand that it’s all about the content. That’s why we have high-yield practice questions written and screened by high-performing physician authors that are updated on a regular basis to ensure our SmartBanks stay up-to-date with exam blueprint changes. Below is a free USMLE Step 2 CK sample question so you can see what we mean.
Your First Free Step 2 Sample Question
A 13-year-old girl is brought to the emergency department because of a 12-hour history of fever and sharp chest pain that worsens with deep breathing. During the past 4 days, she has had intermittent episodes of moderate pain in her right knee, left ankle, and right elbow. She also has had marked fatigue. Three weeks ago, she had a sore throat and fever that resolved spontaneously after a few days and did not require treatment. Medical history otherwise is unremarkable and she takes no medications. She has no known sick contacts. Her vaccinations are up-to-date. She lives in California but has traveled to North Carolina and Japan within the past 12 months. She has a boyfriend but says that she is not sexually active. Her temperature is 38.5°C (101.4°F), pulse is 80/min, and blood pressure is 108/65 mm Hg. On physical examination, the oropharynx is nonerythematous. No tonsillar enlargement, exudate, or palatal lesions are noted. Breath sounds are clear bilaterally. Cardiac auscultation discloses a pericardial friction rub.
Laboratory studies show:
| Hemoglobin | 13.8 g/dL |
| Leukocyte count | 9,800/mm3 |
| Platelet count | 230,000/mm3 |
| Creatinine | 0.9 mg/dL |
| Erythrocyte sedimentation rate | 71 mm/h |
ECG shows diffuse ST-segment elevations and a prolonged PR interval. Which of the following is the most likely causal organism?
- A. Coxsackievirus
- B. Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- C. Rickettsia rickettsii
- D. Streptococcus pyogenes
- E. Trypanosoma cruzi
Answer and Explanation
The correct answer is: D
| Acute Rheumatic Fever | ||
| Epidemiology | Peak age: 5-15 years Girls > boys | |
| Cause | Typically occurs 2-4 weeks after untreated group A streptococcus pharyngeal infection Type II hypersensitivity reaction | |
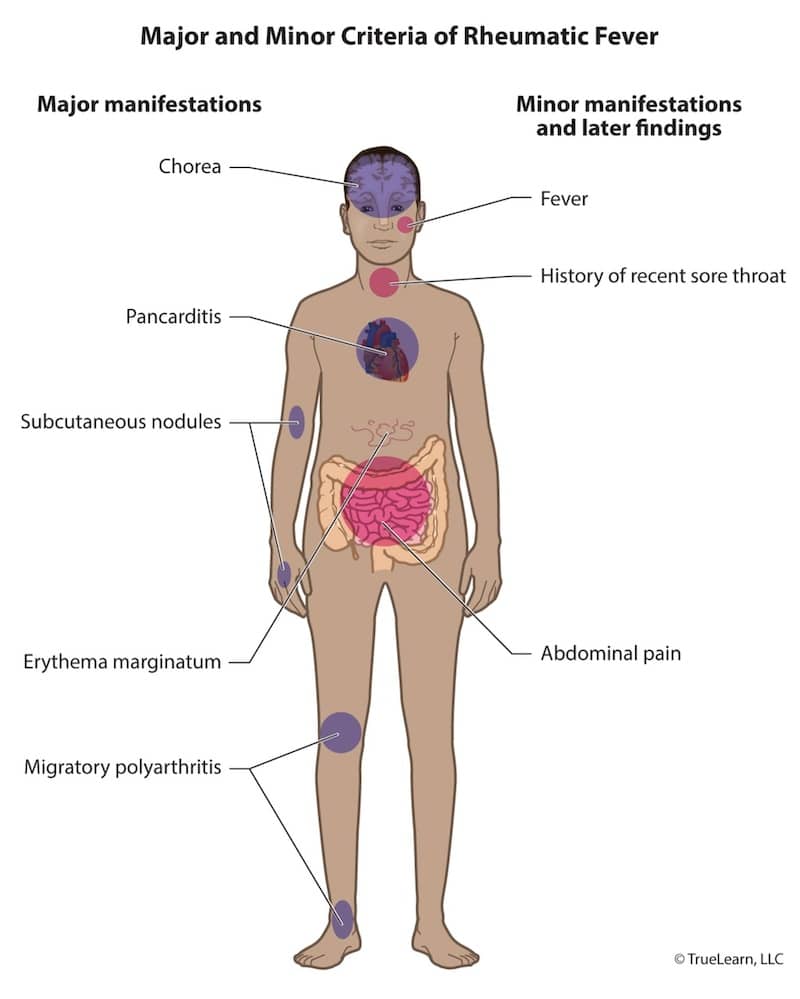
| Clinical Features | Major criteria | Joints: Migratory arthritis ♥: PancarditisNodules (subcutaneous) Erythema marginatum Sydenham chorea (central nervous system involvement) |
| Minor criteria | Arthralgias Fever Increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate and/or C-reactive protein Prolonged PR interval on ECG | |
| Late Complications | Mitral valve disease (regurgitation or stenosis) | |
| Prevention | Penicillin for group A streptococcal pharyngitis | |
This patient likely has acute rheumatic fever (ARF), which occurs as a complication of untreated pharyngeal infection with Streptococcus pyogenes (group A streptococcus).
ARF is an immune-mediated disease (type II hypersensitivity reaction) that occurs when antibodies to the M protein of S pyogenes cross-react with self antigens (molecular mimicry). It occurs most commonly in girls aged 5 to 15 years and symptoms typically appear 2 to 4 weeks following untreated streptococcal pharyngitis. The exact presentation of ARF can vary but the diagnosis can be made if the patient has two major Jones criteria, one major and two minor Jones criteria, or if carditis or Sydenham chorea is present. This patient presents with carditis (ie, friction rub, diffuse ST-segment elevation, prolonged PR interval), migratory arthritis, fever, and an increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
Treatment of ARF involves supportive care. Note that antibiotics typically are not used because symptoms are the result of an immune-mediated response, not bacteremia. ARF can be prevented with penicillin treatment of streptococcal pharyngitis.
*Note that acute post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis also develops 2 to 4 weeks after streptococcal pharyngitis. However, unlike ARF, acute post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis cannot be prevented with penicillin.
Incorrect Answer Explanations
Answer A: Although coxsackievirus is the most common cause of pericarditis and myocarditis, it does not account for this patient’s migratory joint pain. Make sure that your answer choice can explain each aspect of the patient’s presentation.
Answer B: Neisseria gonorrhoeae infection can cause diffuse joint pain and fever. Although this patient says that she is not sexually active, she could be lying. Patients with gonococcal infection, however, do not present with carditis as seen in this patient, making gonococcal infection unlikely.
Answer C: Rocky Mountain spotted fever (RMSF) is a tick-borne illness caused by Rickettsia rickettsii. Infection is seen most commonly in the South Atlantic states, especially North Carolina. Patients typically present with a triad of headache, fever, and rash (because of vasculitis). The rash characteristically starts at the wrists and ankles before spreading to the trunk, palms, and soles. Although this patient has traveled to North Carolina, her symptoms are not consistent with the classic presentation of RMSF (which is most likely to be tested on the examination), and RMSF does not explain her carditis.
Answer E: Chagas disease is caused by the protozoal organism Trypanosoma cruzi and is seen most commonly in Central and South America. Patients typically present with signs of heart failure secondary to dilated cardiomyopathy. Additional signs can include colonomegaly and/or achalasia. This patient has traveled to Japan and North Carolina, not Central and South America, and her cardiac symptoms suggest carditis, not heart failure.
Bottom Line
Patients with acute rheumatic fever most commonly present 2 to 4 weeks after an untreated episode of streptococcal pharyngitis. Common signs include carditis, migratory arthritis, subcutaneous nodules, erythema marginatum, and sydenham chorea.
TrueLearn Insight
Don’t assume that the patient’s travel history is always a clue to the correct answer choice. On the Step 2 CK and shelf examinations, travel history is one of the most commonly used distractors. Although you always should consider an answer choice that seems related to the travel, you should not choose it as the correct answer based on the travel history alone. Instead, make sure that the answer also can explain the other details (eg, symptoms, examination findings, laboratory findings) that were presented in the stem. If it can’t, then the travel history is most likely included to throw you off track.
For more information, see:
- Acute rheumatic fever: clinical manifestations and diagnosis: UpToDate
- Szczygielska I, Hernik E, Kolodziejczyk B, Gazda A, Maslinska M, Gietka P. Rheumatic fever – new diagnostic criteria. Reumatologia. 2018;56(1):37-41.
More Free Step 2 Sample Questions
Want more TrueLearn USMLE Step 2 sk sample questions? Sign-up for a free trial to get access to SmartBanks. And when you’re ready, come back to check out our Step 2 q-bank.