Cultivating Self-Directed Learning Among Nursing Students for Long-Term Success
Self-directed learning (SDL) has been found to have a significant positive effect on both clinical competence and the clinical learning environment. Research shows that when nursing students engage in SDL, they not only build essential clinical skills but also adapt more effectively to the demands of real-world healthcare settings.1 By empowering students to take charge of their own learning, SDL fosters resilience, confidence, and a proactive approach to patient care.
For nursing programs, the mission goes beyond preparing students to pass the NCLEX®. The goal is to prepare future nurses for the complexities of clinical practice, where high-quality patient care depends on a blend of theoretical knowledge, clinical judgment, and agile problem-solving. Today’s nursing students must master rigorous curricula and develop essential competencies—from sound decision-making to quick thinking in high-stakes situations. These skills are vital for delivering patient care with confidence, competence, and adaptability.

For nurse educators, integrating SDL early in the program is one of the most effective ways to support both learning and exam outcomes. When students take ownership of their learning journey, they become more engaged, motivated, and prepared for the challenges of professional practice. Educators play a pivotal role in this process by creating opportunities for students to set meaningful goals, reflect on their progress, and apply their knowledge in ways that enhance clinical readiness.
In this blog, we’ll explore what SDL truly entails, its benefits, the challenges it presents, and practical strategies for integrating SDL into nursing education. We’ll also discuss how technology can enhance SDL, empowering educators to better prepare students to meet the demands of modern healthcare with confidence and competence.
The Importance of Self-Directed Learning in Nursing Education
Self-directed learning (SDL) is a learner-centered approach where students take control of their own educational journey, actively engaging in setting learning objectives, identifying strategies, evaluating progress, and making adjustments as needed. Students assess their knowledge gaps, set personal goals, and select learning strategies that align with their individual needs.
This approach fosters autonomy, resilience, and the ability to adapt, which are all critical qualities for nursing professionals who must navigate the complexities of patient care in rapidly evolving healthcare environments.
How Self-Directed Learning Benefits Students, Faculty, and Programs
The benefits of SDL go far beyond academic achievement; it also helps build a strong foundation of essential clinical competencies that prepare students for real-world practice.
For Students
- Enhance Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving: SDL requires students to actively apply knowledge to real-world scenarios, strengthening critical thinking and problem-solving skills essential for patient care.
- Increase Motivation and Engagement: When students take charge of their learning, they naturally become more motivated and engaged, promoting resilience and adaptability that helps them thrive in healthcare environments.
- Improve Clinical Judgment: SDL fosters self-awareness and reflective practice, leading to sharper clinical judgment and more patient-centered decision-making—skills critical for safe, effective Nursing practice.
- Preparedness for Lifelong Learning: With SDL, students develop habits of continuous learning and self-assessment, equipping them to stay current in an ever-evolving field and positioning them for long-term professional growth.
For Faculty
- Reduce Time on Reviewing Foundational Content: With students actively engaged in SDL, faculty can rely on students to review foundational material on their own, freeing up instructional time for advanced discussions and clinical applications.
- Greater Depth in Course Content: SDL allows faculty to focus on complex topics and challenging clinical scenarios, knowing students are better prepared for higher-level content.
- Improve Course Outcomes: As students take ownership of their learning, their understanding deepens, and course outcomes improve.
- Streamline Workload for Faculty: SDL empowers students to manage their own progress, allowing faculty to reduce repetitive instruction.
For Nursing Programs
- Reduced Student Attrition: Early integration of SDL can help reduce student attrition by building resilience, adaptability, and a proactive approach to learning.
- Improved Graduation Rates: By fostering self-regulation, SDL enables students to stay on track, meet key milestones, and confidently progress toward graduation.
- Enhanced First-Time Pass Rates on the NCLEX®: Through SDL, students build critical thinking, clinical judgment, and self-assessment skills essential for the NCLEX®.
Challenges of Self-Directed Learning
While SDL offers numerous benefits, implementing it effectively in nursing programs comes with a few key challenges:
- Time Management and Prioritization Skills: SDL requires students to manage their own time and set priorities effectively, a skill set that may be underdeveloped in some Nursing students.
- Faculty Bandwidth for Support and Guidance: Fostering SDL in the curriculum requires a balance of independence and support, but faculty may have limited capacity to provide consistent guidance.
- Objective Assessment of Progress: Both students and faculty may lack insights into learning progress, making it hard to gauge competency accurately.
Strategies for Fostering Self-Directed Learning in Nursing Students
To overcome the challenges associated with SDL and effectively foster it, nursing programs can implement targeted teaching strategies that create a learning environment supporting autonomy, resilience, and clinical competence in nursing students. Here are some effective teaching strategies educators can use:
1. Engage Students in a Multimodal Approach
A multimodal teaching approach creates an engaging and inclusive learning environment using diverse methods to meet varied learning preferences. Techniques like the multimedia principle (combining visuals with text) and audio-visual mnemonics empower faster learning, better retention, and easier recall, breaking down complex concepts into memorable lessons.
In both classroom and clinical settings, educators can enhance learning by using active learning tools such as augmented reality, 3D models, online quizzes, and data-driven assessment tools. Leveraging varied modes of delivery ensures that learners are equipped with a solid foundation of knowledge, enabling them to develop higher-order thinking and critical skills essential for long-term learning success in healthcare.
2. Facilitate Metacognition, Self-Regulation, and a Growth Mindset
The facilitation of active learning has been shown to support better long-term retention—essential for building schema and a strong foundational knowledge base—and to create an environment where learners can engage in metacognition, self-regulated learning (SRL), and a growth mindset.
Metacognition, the ability to monitor and control one’s learning, is a teachable skill that can be integrated through active learning tools like audio-visual mnemonics, practice questions, reflection assignments, and scaffolding. These techniques enhance memory, knowledge retrieval, and deeper thinking, equipping students with stronger critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
SRL empowers students to set goals, track progress, and reflect on outcomes in a cyclical process that encourages active involvement in their own learning journey and allows for continuous improvement.
A growth mindset—the belief that intelligence can develop through effort—promotes resilience and academic success. Unlike a fixed mindset, it allows students to embrace challenges and persist through setbacks. With a supportive learning environment that encourages SRL and growth, students are more motivated, which positively impacts their learning and performance.
3. Leverage Self-Reflective Assessments
Self-reflective assessments—structured exercises that encourage students to analyze their thoughts, actions, and feelings—engage critical cognitive skills such as description, analysis, evaluation, and planning. When applied in nursing education, self-reflective assessments can increase students’ self-efficacy and engagement, both crucial for high-quality patient care. This practice also fosters lifelong learning habits, improves adherence to ethical standards, and strengthens clinical competency.
By integrating self-reflective assessments into nursing education, programs enable students to build these essential qualities from day one, helping them refine their skills throughout their journey to licensure and into professional practice.
4. Use Evidence-Based Strategies Such As Quizzing
Retrieval practice and spaced repetition are proven methods for improving learning, performance, and retention. When combined, these strategies create a powerful “spacing-retrieval” effect that enhances memory encoding, long-term knowledge retention, and easy recall more effectively than either strategy alone.
Quizzing leverages this combined effect by providing a flexible and adaptable tool that can be customized in format, content, and difficulty to meet students’ individual needs, strengths, and learning goals. Quizzes can be used as classroom activities, individual assignments, paired with reading materials, or as formative and summative assessments. This adaptability allows quizzing to serve a dual purpose: assessing students’ current knowledge while reinforcing comprehension and mastery.
5. Utilize Technology to Enhance Self-Directed Learning
Technology offers powerful tools to support self-directed learning (SDL) by providing students with interactive, adaptable learning experiences. With the right resources, nursing students can reinforce knowledge, track progress, and focus on areas needing improvement—all essential for building confidence and clinical readiness.
One effective and proven technology solution to enhance SDL is the Picmonic-TrueLearn learning loop. This integrated approach combines Picmonic’s audio-visual mnemonics with TrueLearn’s adaptive assessment platform to drive knowledge acquisition, retention, and application. Using memory science, spaced repetition, and retrieval practice, Picmonic makes complex concepts memorable and boosts long-term retention. TrueLearn complements this by reinforcing critical thinking and knowledge application through board-style questions and adaptive technology. Together, the learning loop empowers students to build the lasting knowledge and clinical skills essential for success in exams and practice.
How The Picmonic-TrueLearn Learning Loop Engages Students in Self-Directed Learning
Picmonic provides an interactive, multimedia approach to mastering complex nursing concepts. Using visual aids, humor, and structured study tools, it leverages cognitive science strategies to support self-directed learning (SDL) and boost memory retention. Here’s how Picmonic empowers students to take control of their learning journey:
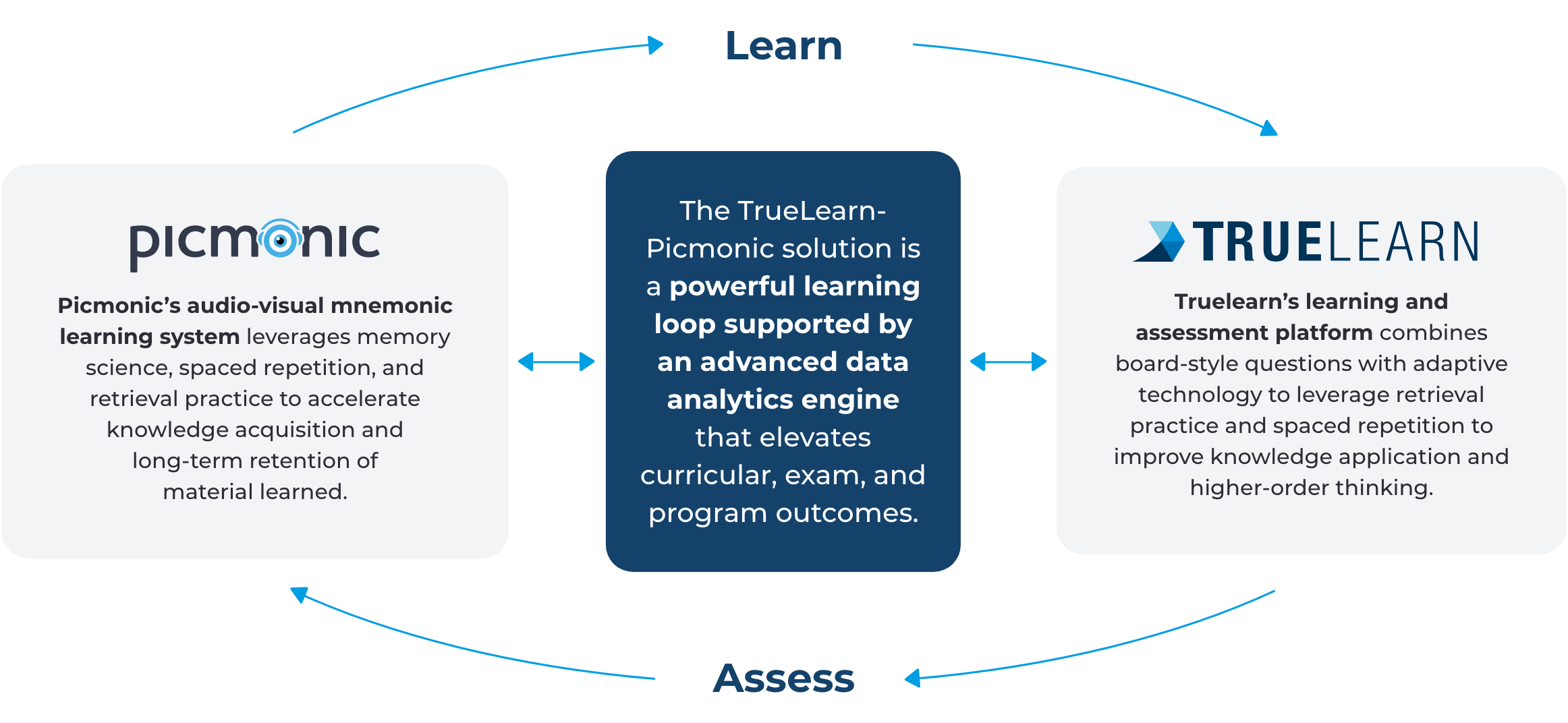
- Audio-Visual Mnemonics Mapped to Curriculum: Picmonic breaks down complex Nursing concepts into memorable, audio-visual mnemonics aligned with popular textbooks, using humor and storytelling to support cognitive retention.
- Customizable Study Plans: Students can create personalized study schedules within Picmonic, encouraging effective time management and goal-setting—core SDL skills.
- Data-Driven Recommendations: Picmonic’s analytics identify areas needing reinforcement, allowing students to target weak points and focus on high-impact content for mastery.
Learn how a nurse educator in Virginia found great success with Picmonic, powered by TrueLearn, as a teaching tool.
Learn HowWhile Picmonic builds foundational knowledge through engaging mnemonics, TrueLearn enhances self-directed learning by enabling students to apply their knowledge in realistic practice exam scenarios. Utilizing adaptive technology and personalized goal-setting, TrueLearn sharpens critical thinking and keeps students focused on their objectives. Here are some ways TrueLearn enables students to maximize their learning potential:
- High-Yield, Exam-Aligned Practice Questions: TrueLearn’s SmartBank aligns with NCLEX-RN® blueprint, simulating real exam conditions to build confidence and readiness.
- Goal-Setting and Progress Tracking: Students set learning goals and track progress against national benchmarks, motivating them to meet milestones as they prepare for exams.
- Adaptive SmartTools for Efficient Learning: TrueLearn’s adaptive tools and analytics personalize study sessions, helping students address studying and testing behaviors to improve test-taking skills, and help address weak content areas and overall learning for better retention and understanding.
- Supporting Faculty and Program Leaders with Comprehensive Analytics: Beyond enhancing student learning, the Picmonic-TrueLearn learning loop provides faculty and program leaders with comprehensive analytics to monitor progress, address learning gaps, and optimize curriculum effectiveness. These insights empower educators to make data-informed decisions that drive program outcomes and student success.
- Detailed Insights by Category and Topic: Faculty access in-depth performance data, enabling focused interventions where students need the most support.
- Longitudinal Tracking Across Programs and Cohorts: Faculty can track student performance across cohorts and time, allowing for curriculum adjustments based on program-specific data insights.
By cultivating nursing students as self-directed learners, educators support the development of lifelong learning habits essential for both personal and professional growth. This approach enables students to strengthen their understanding and adherence to ethical standards, improve clinical competency, and ultimately deliver high-quality patient care in the future. To achieve this, nurse educators need access to the right tools and technology to empower their students effectively.
Explore how Picmonic, powered by TrueLearn, can help your program elevate nursing student learning and outcomes.
Learn HowReferences & Footnotes
1 Vasli P, Asadiparvar-Masouleh H. Self-directed learning and clinical competence: The mediating role of the clinical learning environment.
J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2024;19(2):221-232.doi:10.1016/j.jtumed.2023.11.004.
*NCLEX® is a registered trademark of the National Council of State Boards of Nursing (NCSBN). This content is not endorsed or approved by the NCSBN.


